- Joined
- Oct 9, 2025
- Messages
- 38
Module 1: Introduction to PHP & Web Development
Welcome to your PHP course! We'll go module by module as requested. Starting with Module 1.
1.1 What is PHP and Why Learn It?
PHP (which stands for PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor) is a popular open-source server-side scripting language specifically designed for web development. It allows you to create dynamic web pages by embedding code directly into HTML. When a user visits a PHP-powered page, the server executes the PHP code and generates HTML output sent to the browser.

Why learn PHP in 2025?
- Massive popularity: PHP powers around 74-77% of websites with a known server-side language (e.g., WordPress, which runs ~43% of the entire web, is built on PHP).
- Huge ecosystem: Frameworks like Laravel and Symfony make modern development fast, secure, and enjoyable.
- Job opportunities: Strong demand for PHP developers, especially in CMS (WordPress/Drupal), e-commerce, and backend roles.
- Easy to learn: Beginner-friendly syntax, similar to C/JavaScript.
- Continuous evolution: PHP 8+ is fast, modern, and performant (with features like JIT compilation).
- Community & resources: Vast free tutorials, tools, and libraries.
PHP isn't "dead"—it's a mature, reliable workhorse for the web.
1.2 PHP History and Evolution (PHP 5, 7, 8+)
PHP was created in 1994 by Rasmus Lerdorf as a simple set of tools for his personal homepage. It evolved rapidly:- Early versions (1-4): Basic scripting, became popular for dynamic sites.
- PHP 5 (2004): Introduced major OOP improvements, better performance.
- PHP 7 (2015): Huge leap—up to 2x faster than PHP 5, scalar type hints, better error handling.
- PHP 8 (2020+): Modern features like JIT (Just-In-Time compilation for speed), attributes, match expressions, union types, enums (8.1+), and more. PHP 8.3/8.4 added refinements; as of late 2025, PHP 8.5 is the latest stable version.
The jump from 5 to 7 fixed many old issues, and 8+ made PHP competitive with newer languages. Today, focus on PHP 8+ for new projects—older versions like 7 are unsupported and insecure.
1.3 Setting Up Development Environment
You need a local setup with:
- Web server (Apache/Nginx)
- PHP interpreter
- Database (MySQL/MariaDB)
- Tools like phpMyAdmin (optional)
XAMPP/WAMP/MAMP vs Docker
- XAMPP (cross-platform), WAMP (Windows), MAMP (Mac): All-in-one packages that install Apache, MySQL, PHP, Perl quickly. Great for beginners—simple installer, control panel to start/stop services.

Pros: Easy setup, no config needed initially.Cons: Harder to switch PHP versions, less like production (real servers use Linux), potential conflicts with other software.
- Docker: Container-based. Run isolated environments with exact versions (e.g., PHP 8.5 + Nginx + MySQL).


Pros: Portable (same on Windows/Mac/Linux), matches production closely, easy multi-project/version support, modern best practice.Cons: Slight learning curve (Docker Compose files).
Recommendation for 2025:
- Beginners: Start with XAMPP for simplicity.
- As you progress (or for serious projects): Switch to Docker—it's the industry standard and future-proof.
Quick XAMPP setup:
- Download from apachefriends.org (choose latest with PHP 8+).
- Install and launch control panel.
- Start Apache + MySQL.
Local vs Remote Development
- Local: Everything on your machine—fast, offline, no internet needed. Ideal for learning/testing.
- Remote: Code on a server (e.g., via VS Code Remote, or cloud like Laravel Forge/AWS). Better for team collaboration/production-like testing, but slower and needs internet.
Start local!
1.4 Your First PHP Script
Create a file index.php in your XAMPP htdocs folder (e.g., C:\xampp\htdocs on Windows).PHP
PHP:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My First PHP Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello from PHP!</h1>
<?php
echo "The current date and time is: " . date('Y-m-d H:i:s');
phpinfo(); // Shows PHP config (remove later)
?>
</body>
</html>Visit http://localhost/index.php in your browser. You should see the output!
1.5 How PHP Works with HTML/CSS/JavaScript
PHP embeds in HTML using <?php ... ?> tags. It runs on the server:- Generates dynamic HTML.
- CSS/JS remain client-side (browser).
- Example: Use PHP to output dynamic CSS classes or JS variables.
PHP is backend; HTML/CSS/JS are frontend. Together, they build full sites.
1.6 Understanding Client-Server Architecture
Web apps follow the client-server model:- Client (browser): Requests pages, renders HTML/CSS/JS.
- Server (e.g., Apache + PHP): Processes requests, runs PHP code, queries database, sends response.
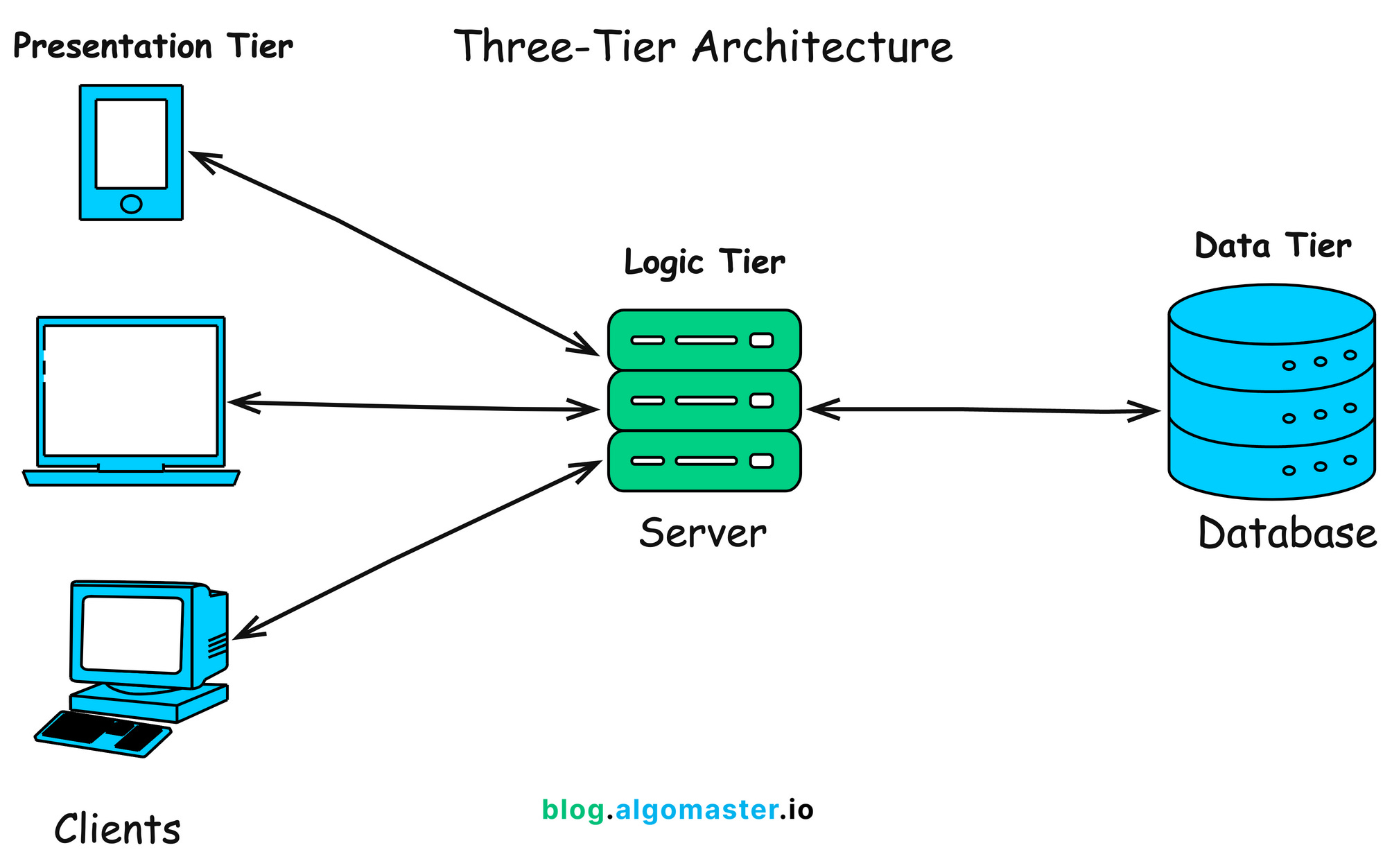
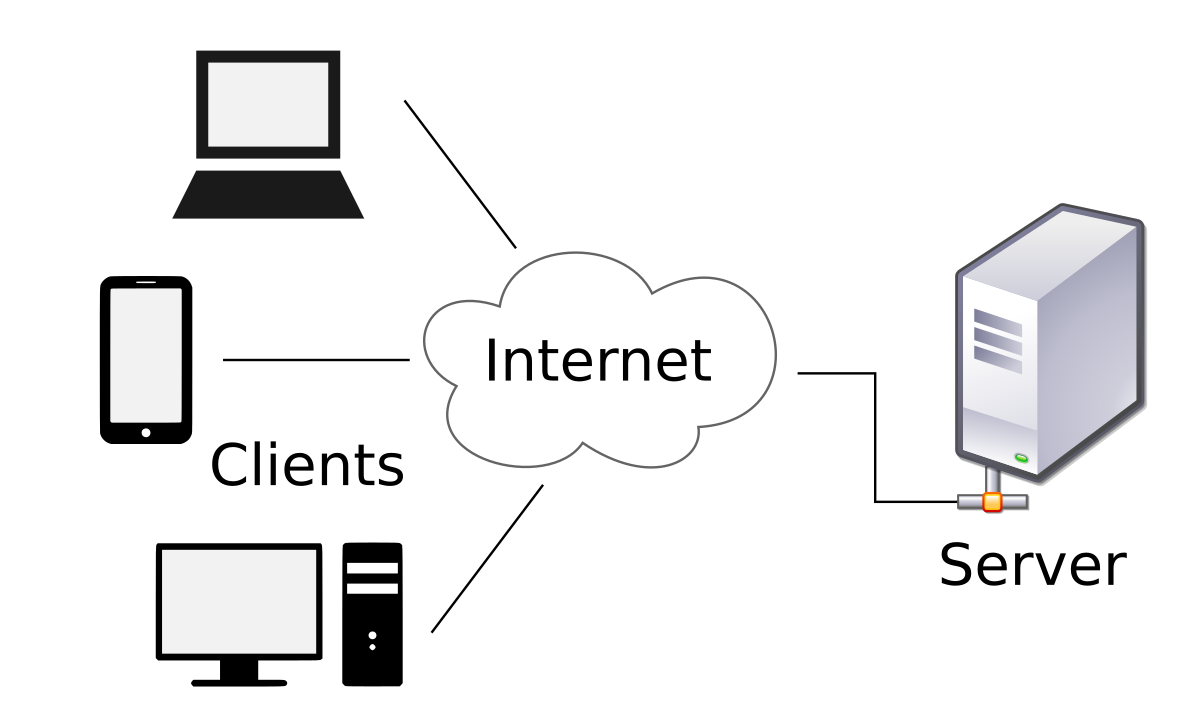
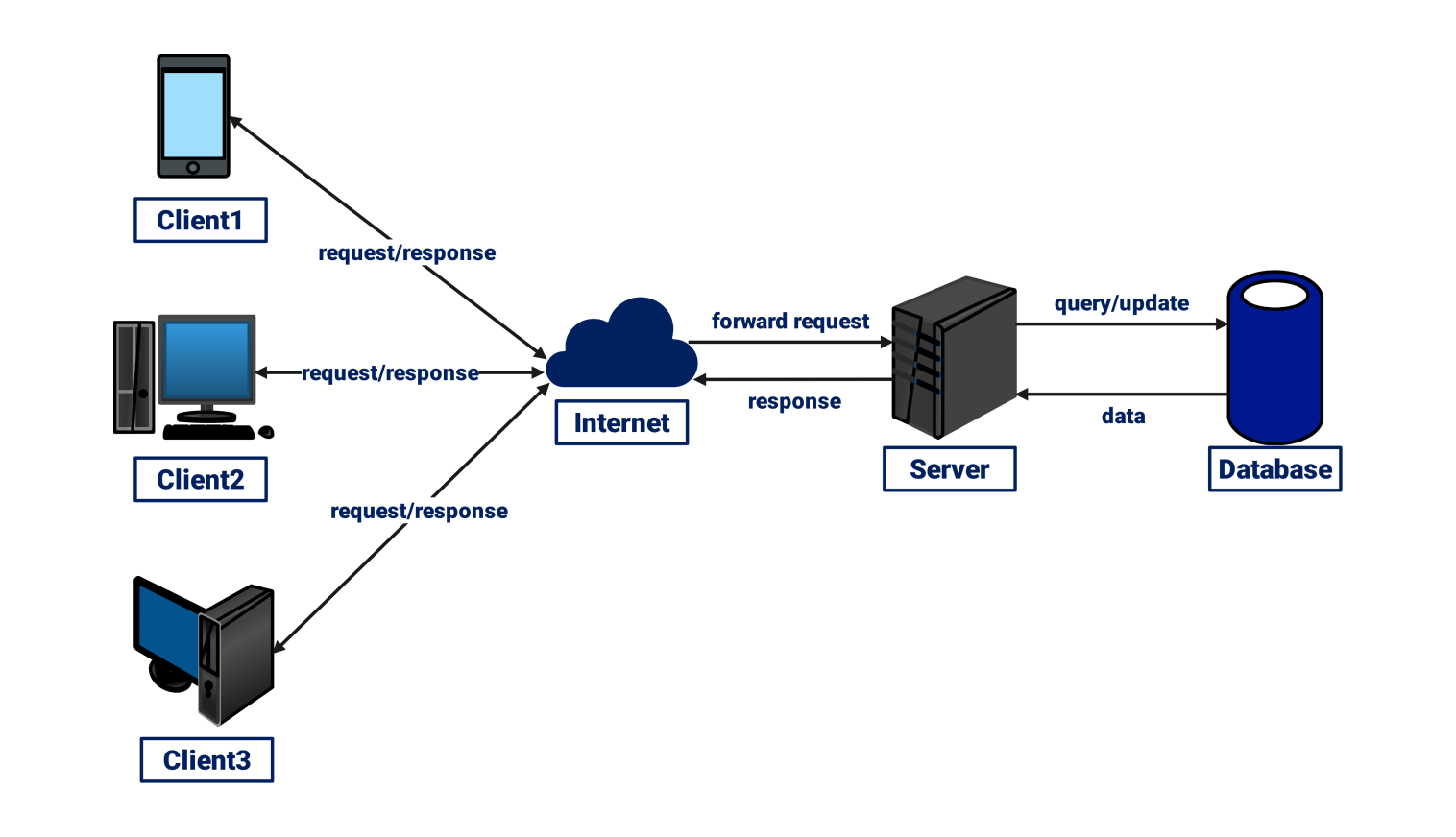
- Browser sends request (e.g., GET /page.php).
- Server executes PHP.
- PHP may interact with DB/files.
- Server sends HTML response.
- Browser displays it.
End of Module 1. Practice your first script, explore phpinfo(), and get comfortable with your setup.
